Learn English French German Hungarian Italian Japanese Korean Mandarin Polish Portuguese Romanian Russian Spanish
Learn from a professional teacher online in a private or group class. Join our free learning community dedicated to language enthusiasts and cultural explorers.
- Take customizable 1-on-1 lessons trusted by thousands of learners
- Learn from certified teachers that fit your budget and schedule
- Connect with a global community of language learners

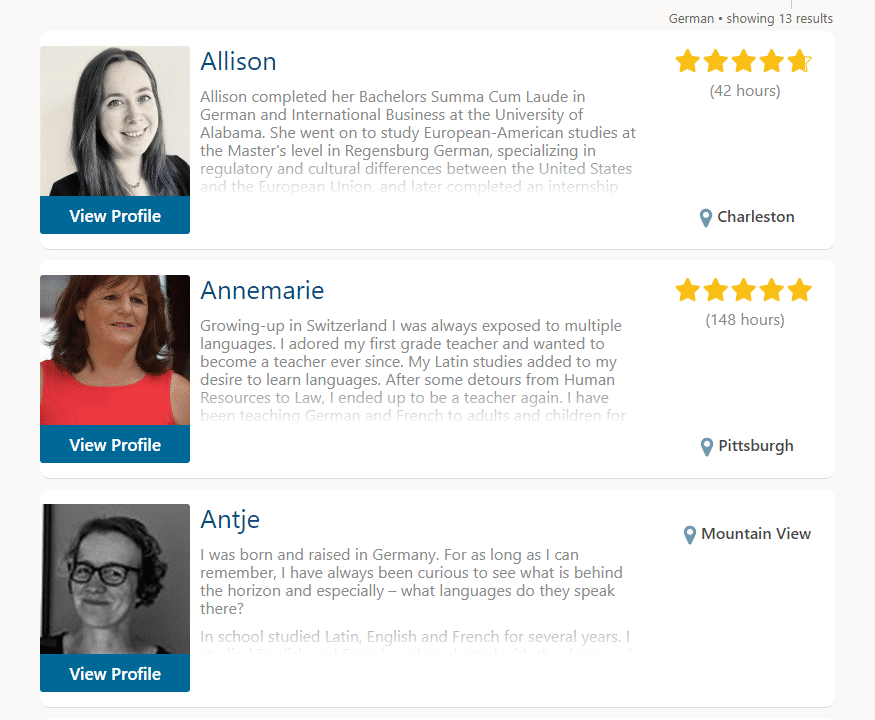
Discover and Request some of our Favorite Teachers
Learn more about our simple flat rate pricing and how to get started HERE.
See what CORE Languages offers
1-on-1 Sessions
Group Sessions
Practice for Free
Hear it from other CORE Languages learners.















Over 60 Languages Offered
Language Training
for your business
Enroll individual employees or start training for your whole team. Learn about our different course options for busy professionals.
















Learning in the Classroom and Beyond
Community
CORE Languages Community
CORE Languages is an engaging online community dedicated to language enthusiasts and cultural explorers. Our free platform provides a vibrant space for individuals to connect, share, and learn about their favorite languages and the rich cultural contexts that surround them. Within CORE Languages, members can join various groups tailored to specific languages and cultural interests, enabling them to engage in meaningful discussions, exchange resources, and collaborate on language learning and cultural exchange.

Professional Teachers
Learn with our best language teachers
Choosing a CORE Languages professional teacher for one-on-one live classes offers a personalized and flexible approach to language learning tailored to your individual needs and schedule. With this option, you can select a qualified instructor who specializes in the language and cultural nuances you're eager to explore. These dedicated professionals work closely with you, adapting their teaching methods to suit your learning style, goals, and proficiency level. The convenience of scheduling classes at times that fit your availability ensures a seamless integration of language learning into your daily routine.
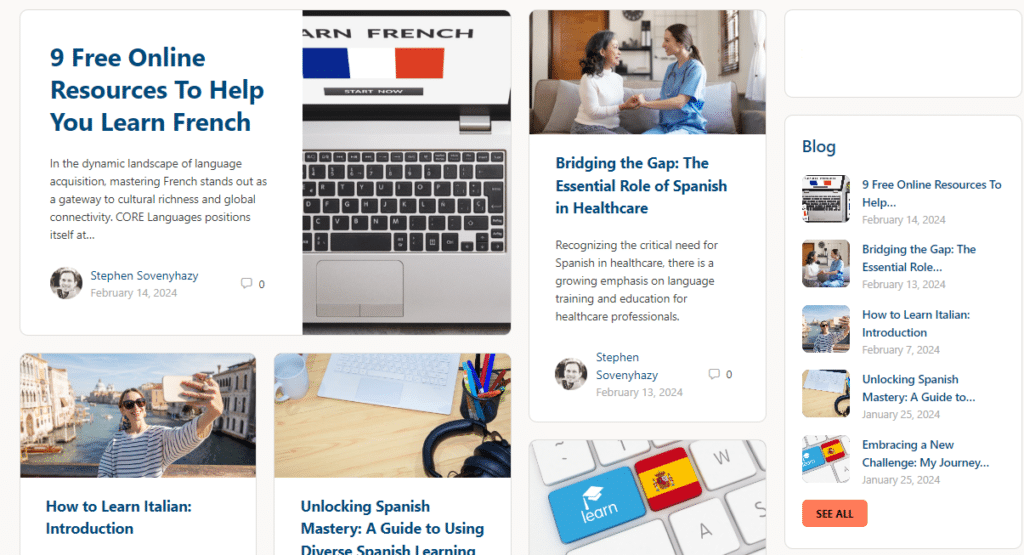
Blog
Read some of our newest articles
The CORE Languages COMPASS Blog is a captivating series of curated articles designed to ignite thoughtful conversation within the online language community. Each piece is carefully selected and crafted to inspire, educate, and engage readers on a variety of topics related to languages, cultures, and global perspectives. From exploring linguistic nuances and cultural traditions to sharing language learning tips and insights into global communication trends, the COMPASS Blog serves as a guiding light for enthusiasts looking to deepen their understanding and appreciation of the world's diverse tapestry of languages and cultures.
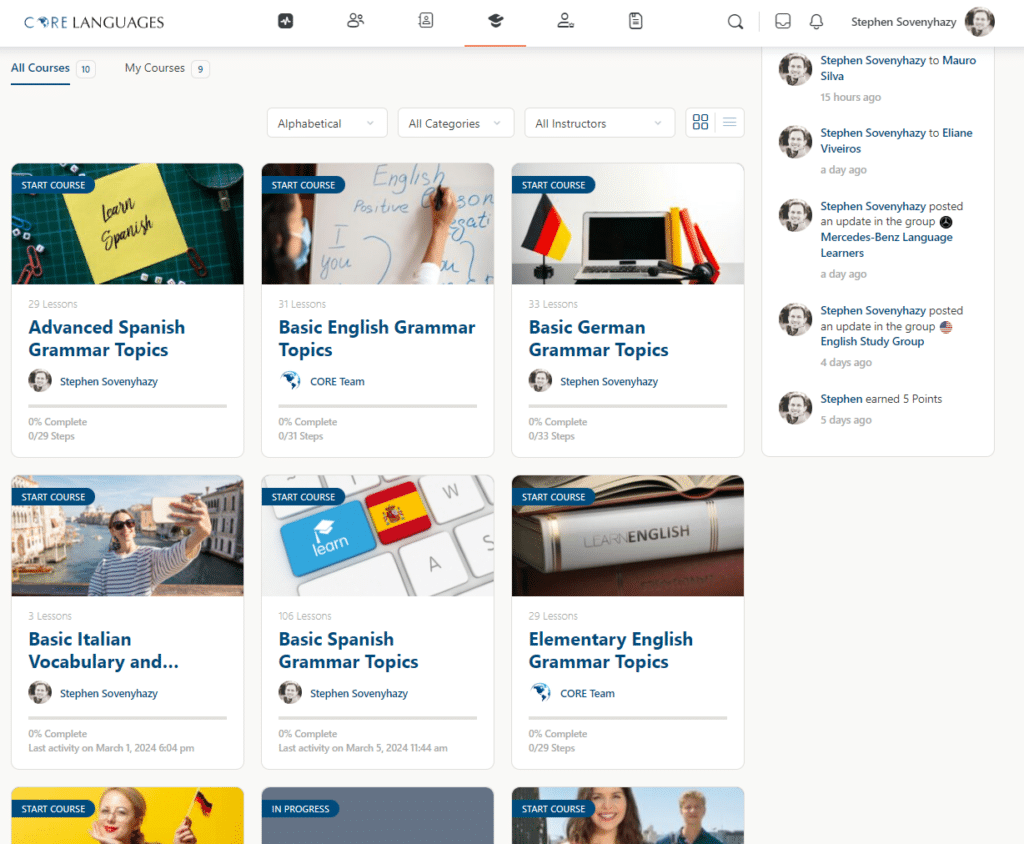
Language Courses
Start learning with Digital Courses
CORE Languages Digital Courses offer an extensive collection of both free and premium learning content, meticulously designed to support and enhance the language learning journey, both within and beyond the live classes led by CORE Languages professional teachers. This comprehensive resource library includes a wide array of interactive modules, videos, quizzes, and downloadable materials tailored to various proficiency levels and language interests. Whether you're reinforcing concepts covered in live sessions, exploring new linguistic territories, or practicing at your own pace, these digital courses provide the flexibility and depth to cater to diverse learning needs.
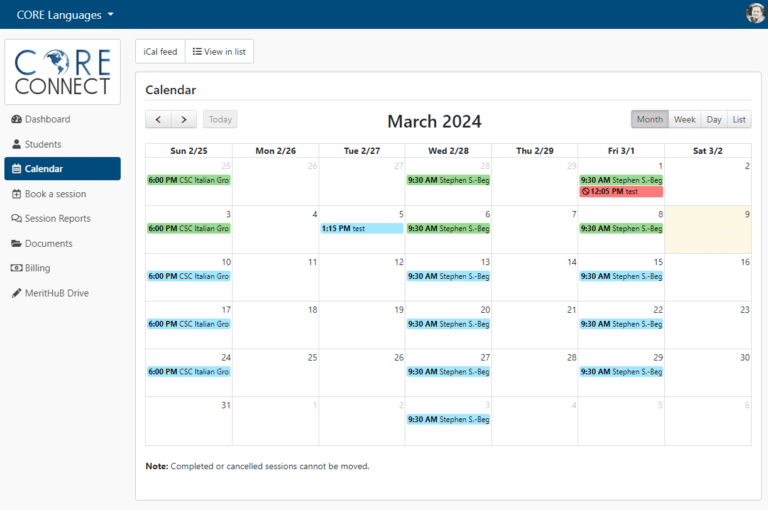
Log Into CORE CONNECT
CORE CONNECT is our scheduling platform for your live classes and sessions. Access your calendar, scheduled sessions, your class recordings and more.